We've joined our RTI Health Solutions colleagues under the RTI Health Solutions brand to offer an expanded set of research and consulting services.
Robust Data Analytics Delivers New Levels Of Population Health Value
The first article in this series covered reasons why population health management (PHM) adoption is accelerating and ways healthcare organizations can mature their PHM data models.
Now, in part two, we're looking at how more sophisticated data analytics capabilities and tools extend PHM value. While mature data models coalesce and provide more variety and types of data, robust analytics is foundational to realizing PHM's potential on outcomes, cost, and engagement.
Analytics is the workhorse of population health management
Figure 1 provides a PHM data model where data analytics is sequentially in the second phase. However, PHM data analytics touches almost every area of population health management. Data analytics is the mainstay of enabling any population health initiative, from identifying patient cohorts to risk stratification or tiering to population pattern analysis to performance and quality reporting. As value-based care and care quality measurement requirements become more complex, sophisticated analytics capabilities are the primary route to achieving PHM goals and knowing that care management objectives are achieved.
Most population health management goals articulate:
- Achieving an understanding of population needs
- Identifying individual patients with those same needs
- Awareness of when needs are critical
- When gaps are present
- Initiating effective interventions at the right time
These all require more mature PHM data analytics.
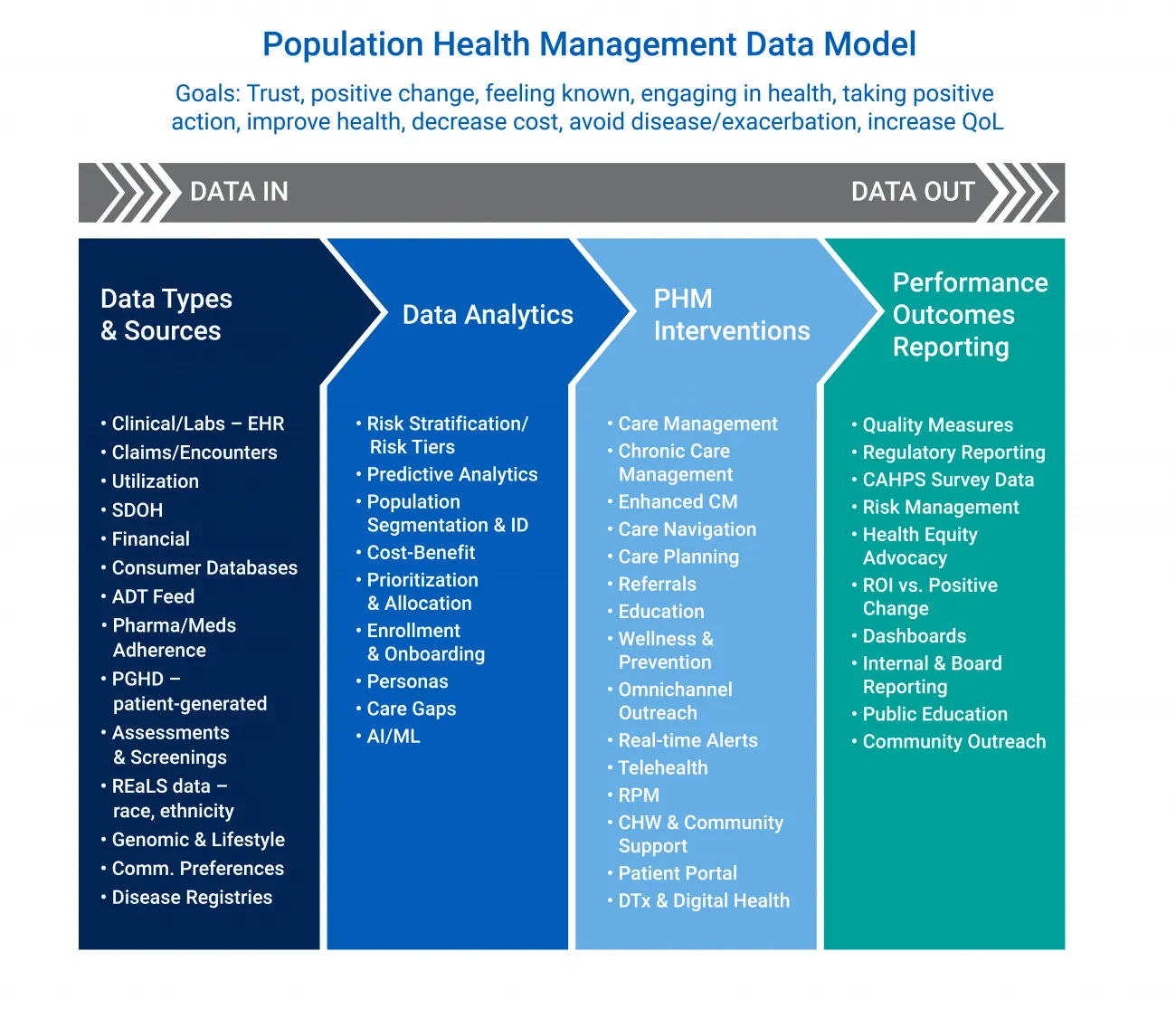
Figure 1: Population Health Management Data Flow Model
Sophisticated data analytics delivers new levels of PHM value
The highest vision of population health achievement relies on mature, integrated, and automated data analytics. While PHM has been around in one form or another since World War II, it became a more formalized approach in the 1980s when public health initiatives worked to go beyond the limitations of individual-oriented clinical methods.
As people live longer, and more individuals are diagnosed with chronic conditions, population patterns reveal opportunities to care for more patients within a specific grouping and apply population discoveries to better care for individuals. Innovations in data science, analytical technologies and tools activate new population health opportunities and achievements, including the following four.
More easily address population and patient-specific needs simultaneously
As the name conveys, PHM has a primary objective to address diseases and health maladies affecting many people. More sophisticated data analytics reveals a broader variety of analytical possibilities around groups of people. It can also be used to gain more significant insights into individual patient health and vice versa.
New and emerging data analytics demonstrate the interrelated and dynamic nature of individuals within a population and patterns in the population that provide context for individual health. Informative contextualization between the two is possible with sophisticated data science.
Activate more data sources at high velocity and in real-time
PHM thrives on data and the discipline is ingesting more from a wider variety of sources than ever before. While more and centralized data holds potential for greater insights, analysis for more real-time or high-volume data sources requires new analytic tools and technologies.
If a healthcare provider or payer wants to have current, comprehensive, and aggregated data-driven PHM, it requires a commensurate level of analytical maturity. Without it, highly-valuable data stagnates and keeps important realizations and opportunities hidden from view or beyond reach of action.
Predictive analytics enables prevention earlier in the healthcare journey
Evolving data analytics capabilities and tools are opening up prevention earlier in an individual's health journey. Previous PHM milestones looked at retrospective data to glean insights on what happened and use that awareness to make decisions about future activities.
PHM's goal, however, is to prevent new or further illness or condition exacerbation and avoid unnecessary care. Interventions are most effective when they are timely, are acted upon quickly, and provided within the context of a broader individual or population health journey.
One example of how past population research enabled predictive analysis is the research conducted in early childhood development. It helped fund and direct program creation in the U.S., but it also provided a rubric that could be used in predictive analysis to reveal population groups and individual children at greatest risk.
Using statistics, quantitative models, and inferential tools coupled with advanced technologies can be an effective combination to estimate the likelihood that an individual will have similar health outcomes as other patients in a population. This type of analysis can find patterns and meaning from disparate data sources and identify groups of providers who make similar decisions or take specific actions.
In a PHM setting, predictive modeling uses data mining, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to recommend an optimal intervention when a patient meets certain population thresholds or patterns that have been proven to lead to likely untoward outcomes.
Using a tool like RTI Rarity™ supports proactive risk identification by measuring and adjusting for behavioral and social factors that impact a person's health. This data identifies those most at risk for lifestyle-driven chronic disease and supports development of targeted preventative interventions.
Leveraging analytics to automate and scale PHM
Population health initiatives are data- and labor-intensive. Data analytics capabilities and tools empower PHM teams to care for more patients at differing acuity levels. It supports this through automating insights and actions, tailoring engagement based on analyzed context and making connections among data points. These are labor-intensive tasks that care managers don't have the time or resources to find manually.
Additionally, advanced analytical tools can relieve some of the burden PHM teams face and focus their efforts on those that require personal engagement and relationships. When these tools are integrated into PHM workflows, they create greater efficiency and employee satisfaction. When they are coupled with automation or intelligent technologies, they can go further to optimize data use, insights, and personalized interventions.
How mature is your PHM data analytics?
Achieving a new level of value for a PHM program from data analytics entails assessing a program's current maturity level and aligning PHM goals with new data analytics capabilities, tools, and skillsets.
Figure 2 shows a model for data analytics maturity levels that can be used as part of that assessment. What types of questions can current data analytics tools, techniques, and skillsets answer now? What should be added to grow to the next level or to the level that matches the types of outcomes needed for population health interventions to achieve program goals?
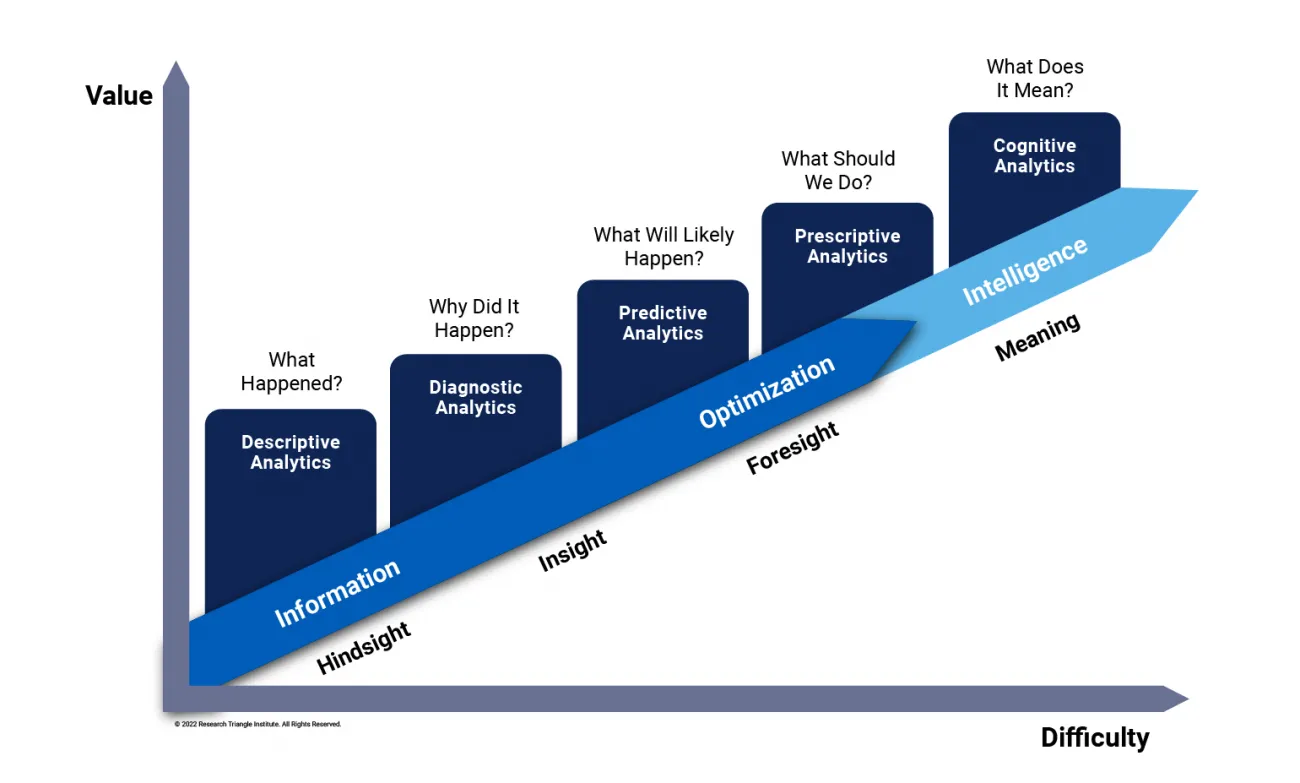
Figure 2: PHM Data Analytics Maturity Levels
RTI Health Advance brings together the power of data analytics, digital health, and patient experience to help provider and payer organizations build population health management programs that are mature and aligned with organizational objectives.
Subscribe Now
Stay up-to-date on our latest thinking. Subscribe to receive blog updates via email.
By submitting this form, I consent to use of my personal information in accordance with the Privacy Policy.